
Configuring BGP on a vRouter
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a path-vector protocol and is the most commonly used routing protocol on the Internet. It advertises the paths required to reach a certain destination. BGP is also a protocol that sits on top of TCP, and is simpler than Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
For example, in Figure 5-2, the network administrator wants to configure network traffic from the source host to reach the destination host. But when different VLANs are configured, the source host traffic is not aware of the route between the source host and the destination host. However, there is a VLAN that spans VLAN 33 and VLAN 55. You can solve this problem by configuring BGP in the same Autonomous System (AS) 100 that sends traffic over VLAN 35. This allows the source host to learn the route to the destination host.
Using a loopback address for peering is useful when there are multiple paths between the BGP peers which would otherwise tear down the BGP session if the physical interface used for establishing the session goes down. It also allows the vRouters running BGP with multiple links between vRouters to load balance over the available paths.
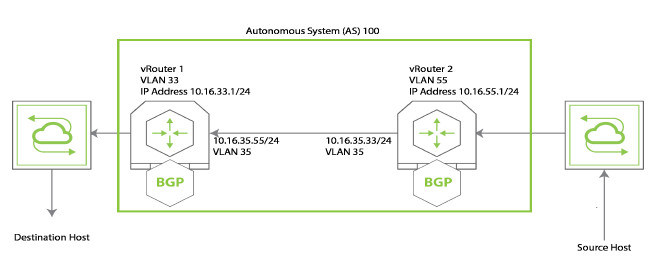
Figure 5-5: Configuring BGP for Two VLANs
This example assumes that you have two VLANs, VLAN33 and VLAN55. Also, that you have added ports to the configuration.
Begin by configuring vRouter1, a software vRouter, on VLAN 33 with the BGP information:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-create name vrouter1 fabricname-global router-type hardware bgp-as 100 bgp-redist-connected-metric none
Additional BGP parameters include the following:
- bgp-redist-static-metric — redistribute static BGP route metric number
- bgp-redist-connected-metric — redistribute connected BGP route metric
- bgp-redist-rip-metric — redistribute BGP into RIP process metric
- bgp-redist-ospf-metric — redistribute BGP into OSPF process metric
- bgp-max-paths — maximum number of BGP paths
- bgp-ibgp-multipath — allow the BGP vRouter to select multiple paths for load sharing.
- bgp-bestpath-as-path — allow BGP to use the best path for traffic forwarding.
- bgp-dampening|no-bgp-dampening — suppress flapping routes so they are not advertised.
- bgp-stalepath-time — how long a router waits before deleting stale routes after an end of record (EOR) message is received from the restarting router.
- bgp-graceful-shutdown|no-bgp-graceful-shutdown— how to configure BGP graceful shutdown (RFC8326)
Add the IP addresses and VLANs:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-interface-add vrouter-name vrouter1 ip 10.16.35.33/24 vlan 35
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-interface-add vrouter-name vrouter1 ip 10.16.33.1/24 vlan 33
Add the BGP information:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-bgp-add vrouter-name vrouter1 neighbor 10.16.35.55 remote-as 100
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-bgp-network-add vrouter-name vrouter1 network 10.16.33.0/24
Display the interface information for vrouter1:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-interface-show format all layout vertical
vrouter-name: vrouter1
nic: eth1.33
ip: 10.9.100.100/16
assignment: static
mac: 66:0e:94:30:c6:92
vlan: 33
vxlan: 0
if: data
alias-on:
exclusive: no
nic-config: enable
nic-state: up
secondary-macs:
vrouter-name: vrouter1
nic: eth2.33
ip: 192.168.42.11/24
assignment: static
mac: 66:0e:94:30:25:5e
vlan: 33
vxlan: 0
if: data
alias-on:
exclusive: no
nic-config: enable
nic-state: up
secondary-macs:
If you want to filter IP hosts, you can add prefix lists to the BGP configuration. See Configuring Prefix Lists for BGP and OSPF.
Then, configure vRouter2 on VLAN 55:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-create name vrouter2 fabricname-global router-type hardware bgp-as 100 bgp-redist-connected-metric none
Add the IP addresses and VLANs:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-interface-add vrouter-name vrouter2 ip 10.16.35.55/24 vlan 35
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-interface-add vrouter-name vrouter2 ip 10.16.55.1/24 vlan 55
Then add the BGP information:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-bgp-add vrouter-name vrouter2 neighbor 10.16.35.33 remote-as 100
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-bgp-network-add vrouter-name vrouter2 network 10.16.55.0/24
And finally, add the loopback address:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-loopback-interface-add vrouter-name vrouter1 index 5 ip 1.1.1.1
Display the vRouter BGP configuration:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-bgp-show format all layout vertical
vrouter-name: vrouter33
ip: 10.16.35.55
neighbor: 10.16.35.55
remote-as: 100
next-hop-self: no
route-reflector-client: no
override-capability: no
soft-reconfig-inbound: no
max-prefix-warn-only: no
vrouter-name: vrouter33
ip: 10.16.33.0
network: 10.16.33.0/24
description: none
vrouter-name: vrouter55
ip: 10.16.35.33
neighbor: 10.16.35.33
remote-as: 100
next-hop-self: no
route-reflector-client: no
override-capability: no
soft-reconfig-inbound: no
max-prefix-warn-only: no
vrouter-name: vrouter55
ip: 10.16.55.0
network: 10.16.55.0/24
description: none
To reset BGP neighbors, use the vrouter-bgp-neighbor-reset command.
To display BGP neighbors, use the vrouter-bgp-neighbor-show command.
CLI (network-admin@switch) > vrouter-bgp-neighbor-show
vrouter-name: vrouter1
neighbor: 10.9.100.201
ver: 4
remote-as: 100
msg_rcvd: 11
msg_sent: 19
tblver: 0
inQ: 0
outQ: 0
up/down: 00:54:04
state/pfxrcd: Connect
remote-router: vrouter2
description: none
vrouter-name: vrouter2
neighbor: 10.9.100.101
ver: 4
remote-as: 100
msg_rcvd: 12
msg_sent: 18
tblver: 0
inQ: 0
outQ: 0
up/down: 00:53:37
state/pfxrcd: Connect
remote-router: vrouter2
description: none
Additional BGP Parameters
There are additional BGP parameters that you can use to optimize your BGP network. Add any of the following parameters:
- ebgp-multihop — a value for external BGP to accept or attempt BGP connections to external peers, not directly connected, on the network. This is a value between 1 and 255.
- update-source vrouter — the source IP address of BGP packets sent by the router. This parameter is required if you want BGP to perform peering over a loopback interface.
- prefix-list-in — specify a list of incoming prefixes for route redistribution.
- prefix-list-out — specify a list of outgoing prefixes for route redistribution.
- override-capability — override the result of capability negotiation with the local configuration. This parameter allows you to ignore a remote peer’s capability value.
- soft-reconfig-inbound — defines the route refresh capability by allowing the local device to reset inbound routing tables dynamically by exchanging route refresh requests to supporting peers.
- max-prefix — allows you to specify the maximum number of IP prefixes to filter.
- max-prefix-warn — add a parameter to warn when the maximum number of prefixes is reached.
