
Configuring IP-based ACLs
In IP-based ACLs the following parameters are available:
- Source IP address
- Source netmask
- Destination IP address
- Destination netmask
- IP Protocol (tcp|udp|icmp|igmp|ip|icmpv6)
- Source Layer 4 Port
- Destination Layer 4 Port
- vNET
- Bridge Domain
- VLAN Number
- Port Number
Using an IP-based ACL to Block IP Traffic
The network example shown in Figure 15-5 - IP-based ACL for Internal Servers below includes a Finance server in one part of the network and an Engineering server in another part.
For example, the network admin may want to block the Engineering server from communicating with the IP protocol with the Finance server in order to protect sensitive company information. For that purpose, you can use an IP-based ACL which can block a specific IP traffic source.
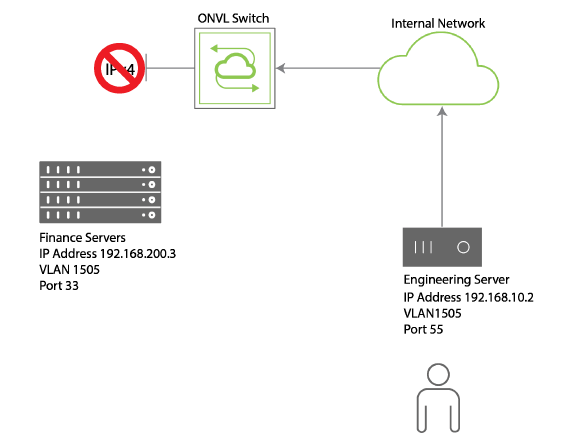
Figure 15-5 - Network Example - IP ACL for Internal Servers
You can use an IP-based ACL also to protect internal devices from external access as depicted in Figure 12-5 – IP-based ACL Blocking External Access below.
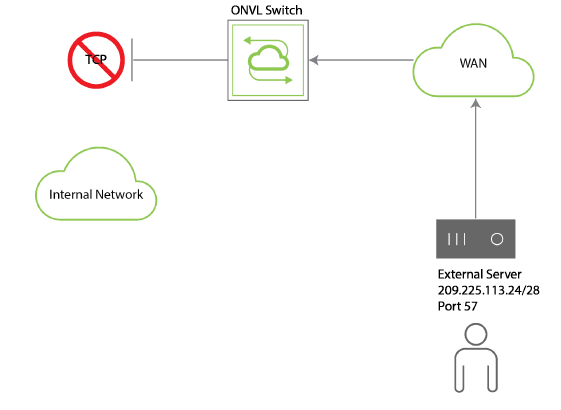
Figure 15-6 - IP ACL Blocking External Access
Configuring an IP-based ACL for Internal Servers
To configure an ACL for denying TCP traffic from the Engineering server to the Finance server you can use the following syntax:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > acl-ip-create name deny-finance action deny scope local src-ip 192.168.10.2 src-ip-mask 24 dst-ip 192.168.200.3 dst-ip-netmask 24 proto tcp src-port 55 dst-port 33 vlan 1505
To review the configuration, use the acl-ip-show command:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > acl-ip-show name deny-finance layout vertical
name: deny-finance
id: b00011:20
action: deny
proto: tcp
src-ip: 192.168.10.2/24
src-port: 55
dst-ip: 192.168.200.3/24
dst-port: 33
vlan: 1505
scope: local
port: 0
Configuring an IP-based ACL Blocking External Access
Referring to Figure 15-5 – IP-based ACL Blocking External Access above, a certain source IP address needs to be blocked.
To configure an ACL to deny traffic from the external server, use the acl-ip-create command to create an ACL named deny-external like so:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > acl-ip-create name deny-external scope fabric src-ip 209.255.113.24/28
To review the configuration, use the acl-ip-show command:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > acl-ip-show name deny-external layout vertical
name: deny-external
id: b000022:20
action: deny
proto: ip
src-ip: 209.225.113.24/28
src-port: 0
dst-ip: ::/0
dst-port: 0
vlan: 0
scope: fabric
port: 0
Configuring an IP-based ACL to Permit Network Traffic
ACLs can be used to permit traffic too: for example, to allow HTTP traffic to the external subnet 209.225.113.24 with a netmask of 255.255.255.240 and a scope of fabric, you can create an IP-based ACL called allow-http using the following syntax:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > acl-ip-create name allow-http permit scope fabric src-ip 0.0.0.0 src-ip-mask 255.255.255.255 dst-ip 209.225.113.24 dst-ip-mask 255.255.255.240 protocol tcp dst-port 57
To review the configuration, use the acl-ip-show command:
CLI (network-admin@switch) > acl-ip-show name allow-http layout vertical
name: allow-http
id: b000025:20
action: allow
proto: tcp
src-ip: 0.0.0.0/255.255.255.255
src-port: 0
dst-ip: 209.225.113.24/28
dst-port: 57
vlan: 0
scope: fabric
port: 0
To delete the ACL, use the acl-ip-delete command.
To modify the ACL configuration, use the acl-ip-modify command.
