
Understanding LAG Path Selection and Load Balancing
For Layer 2 back-to-back connectivity, Arista NetVisor OS supports the standard link aggregation technology in order to combine multiple network connections into a logical pipe called a Link Aggregation Group (LAG), or ‘(port) trunk’, which can provide redundancy in case of single or multiple link failure.
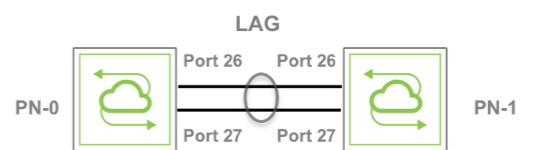
Figure 7-10: Two-port LAG Example
NetVisor OS also supports link aggregation across two redundant chassis to implement multi-pathing without requiring the creation of Layer 2 loops and the use of the Spanning Tree protocol. This feature is called vLAG (Virtual Link Aggregation Group) on a switch cluster.
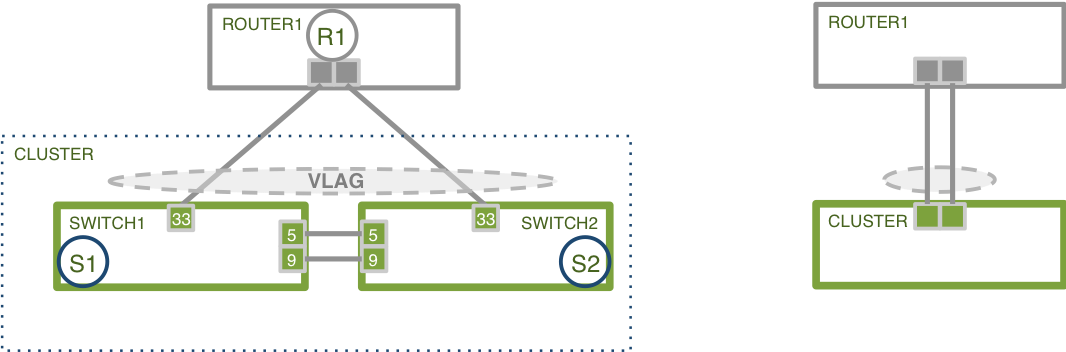
Figure 7-11: Two-port vLAG Example
Both the aforementioned technologies perform path selection in hardware using a high-performance technology called packet field hashing.
What that means is that the hardware extracts a number of packet fields and with them performs a special calculation to generate a hardware index. This hardware index is then used to select an egress physical port for a (v)LAG. Refer to the About Layer 2 Hardware Hashing section for more details on hashing field selection.
