
System - Manage System Settings
Services – System - Manage System Services
There are features and functions used in UNUM Manager and UNUM Analytics that are common throughout the user interface (UI). Please refer to the Common Functions section for more information on the use of these functions and features.
Manage System Services
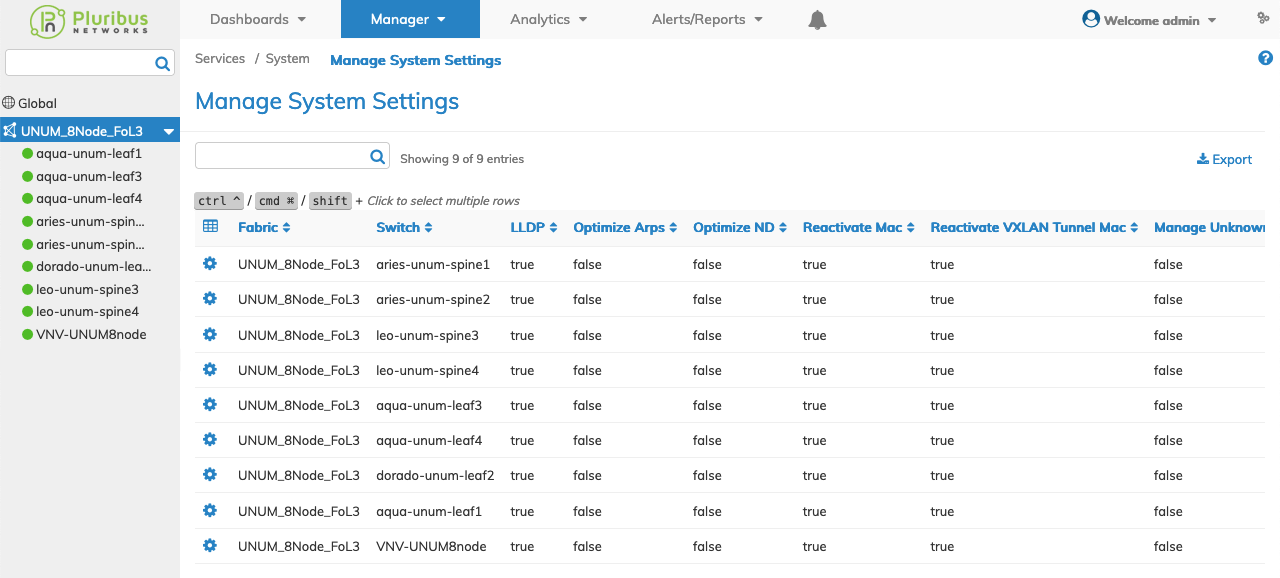
Selecting Manager → Services → Manage System Services displays the Manage System Services dashboard with a list of any existing System settings.
Select the applicable Fabric from the left-hand navigation bar and the dashboard updates showing all Manage System Services entries from all switches within the Fabric.
Note: If no entries exist a "No Data Exists" message is displayed. You must first configure an entry on a switch. Prerequisite settings and configuration may be required.
The dashboard displays a list of existing System Settings entries by Fabric name.
Parameters are described below in Attributes.
Additional System Setting parameters display when selected via the Edit feature (see below).
Fabric Manager Services System - Manage System Settings - Fabric
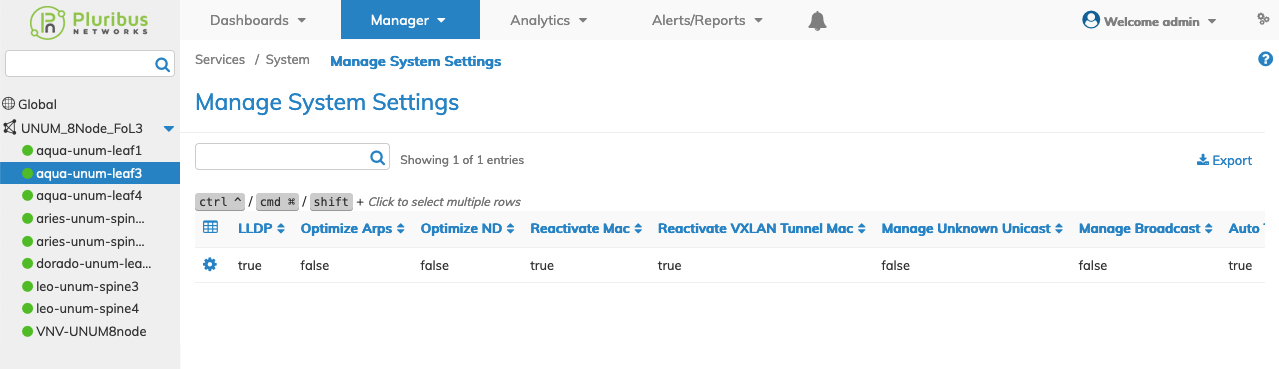
Select the applicable switch from the fabric and the dashboard updates automatically with System Setting entries.
The dashboard displays a list of existing System Setting entries by enabled parameters. See Attributes list below.
Fabric Manager Services System - Manage System Settings - Switch
Attributes include:
|
Fabric |
Switch |
LLDP |
Optimize Arps |
Optimize ND |
Reactivate Mac |
|
Reactivate VXLAN Tunnel Mac |
Manage Unknown Unicast |
Manage Broadcast |
Auto Trunk |
Auto Host Bundle |
Routing Over Vlags |
|
vLE Tracking Timeout |
PFC Buffer Limit |
Snoop Query Stagger |
Proxy Conn Retry |
Proxy Conn Max Retry |
Proxy Conn Retry Interval |
|
NVOS Debug Logging |
XCVR Link Debug |
FastPath BFD |
Linkscan Interval |
Single Pass Flood |
Symmetric Hash |
|
Hash Suppress Unidir Field |
Enable Flow Tracker |
|
|
|
|
Fabric Manager Services System - Manage System Settings - Searchable Attributes
Modify a System Setting
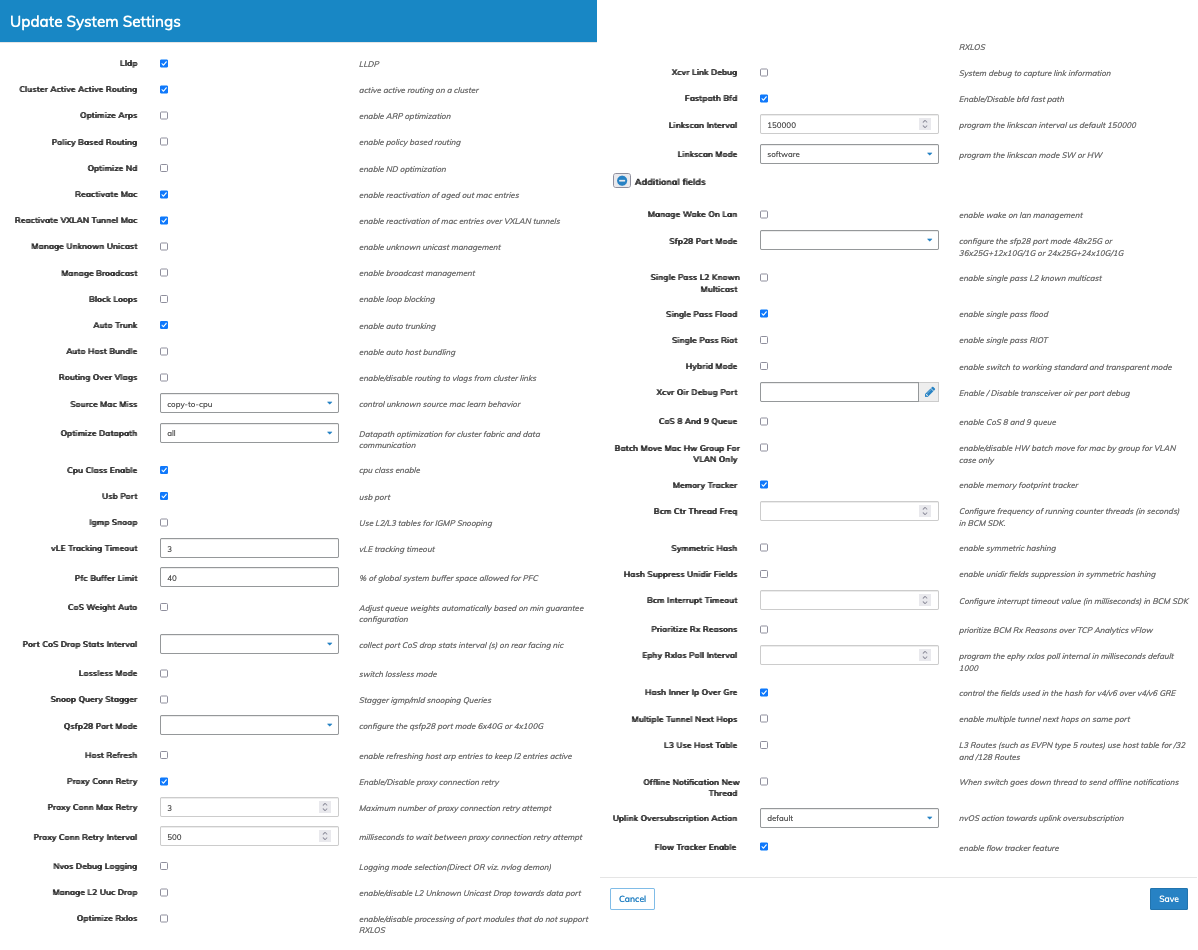
To modify a System Setting click on Edit by selecting the Cog ![]() icon to make changes to the System Setting parameters which include:
icon to make changes to the System Setting parameters which include:
•Lldp – LLDP (checkbox).
•Cluster Active Active Routing – active-active routing on a cluster (checkbox).
•Optimize Arps – enable ARP optimization (checkbox).
•Policy Based Routing – enable policy based routing (checkbox).
•Optimize Nd – enable ND optimization (checkbox).
•Reactivate Mac – enable reactivation of aged out mac entries (checkbox).
•Reactivate Vxlan Tunnel Mac – enable reactivation of mac entries over vxlan tunnels (checkbox).
•Manage Unknown Unicast – enable unknown unicast management (checkbox).
•Manage Broadcast – enable broadcast management (checkbox).
•Block Loops – enable loop blocking (checkbox.)
•Auto Trunk – enable auto trunking (checkbox).
•Auto Host Bundle – enable auto host bundling (checkbox).
•Routing Over Vlags – enable/disable routing to vlags from cluster links (checkbox).
•Source Mac Miss – control unknown source mac learn behavior (selection box).
•Optimize Datapath – Datapath optimization for cluster, fabric and data communication (selection box).
•Cpu Class Enable – cpu class enable (checkbox).
•Usb Port – usb port (checkbox).
•Igmp Snoop – Use L2/L3 tables for IGMP Snooping (checkbox.)
•vLe Tracking Timeout – vle tracking timeout (selection box).
•Pfc Buffer Limit – % of global system buffer space allowed for PFC (selection box).
•Cosq Weight Auto – Adjust queue weights automatically based on min-guarantee configuration (checkbox).
•Port Cos Drop Stats Interval – collect port cos drop stats interval (s) on rear facing nic (selection box).
•Lossless Mode – switch lossless mode (checkbox).
•Snoop Query Stagger – Stagger igmp/mld snooping Queries (checkbox).
•Qsfp28 Port Mode – configure the qsfp28 port mode 6x40G or 4x100G (selection box).
•Host Refresh – enable refreshing host arp entries to keep l2 entries active (checkbox).
•Proxy Conn Retry – Enable/Disable proxy connection retry (checkbox).
•Proxy Conn Max Retry – Maximum number of proxy connection retry attempt (selection box).
•Proxy Conn Retry Interval – milliseconds to wait between proxy connection retry attempt (selection box).
•Nvos Debug Logging – Logging mode selection(Direct OR viz. nvlog demon) (checkbox).
•Manage L2 Uuc Drop – enable/disable L2 Unknown Unicast Drop towards data port (checkbox.)
•Optimize Rxlos – enable/disable processing of port modules that do not support RXLOS (checkbox).
•Xcvr Link Debug – System debug to capture link information (checkbox).
•Fastpath Bfd – Enable/Disable bfd fast path (checkbox).
•Linkscan Interval – program the linkscan interval us, default 150000 (selection box).
•Linkscan Mode – program the linkscan mode SW or HW (selection box).
Select additional field parameters by clicking on the ![]() icon. Additional fields include:
icon. Additional fields include:
•Manage wake on Lan – enable wake on LAN management (checkbox).
•Sfp28 Port Mode – configure the sfp28 port mode 48x25G or 36X25G+12x10G/1G (drop-down list).
•Single Pas L2 Know Multicast – enable single-pass L2 known multi-host (checkbox).
•Single Pass Flood – enable single-pass flood (checkbox).
•Single Pass Riot – enable single-pass RIOT (checkbox).
•Hybrid Mode – enable switch to working standard and transparent mode (checkbox).
•Xcvr Oir Debug Port – Enable / Disable transceiver oir per port debug (interactive port selector).
•Cos 8 And 9 Queue – enable cos-8-and-9-queue (checkbox).
•Batch Move Mac Hw Group For Vlan Only – enable/disable HW batch move for mac by group for VLAN case only (checkbox).
•Memory Tracker – enable memory footprint tracker (checkbox).
•Bcm Ctr Thread Freq – Configure frequency of running counter threads (in seconds) in BCM SDK.
•Symmetric Hash – enable symmetric hashing (checkbox).
•Hash Suppress Unidir Fields – enable unidir fields suppression in symmetric hashing (checkbox).
•Bcm Interrupt Timeout – Configure interrupt timeout value (in milliseconds) in BCM SDK.
•Prioritize Rx Reasons – prioritize BCM Rx Reasons over TCP Analytics vFlow (checkbox).
•Ephy Rxlos Poll Interval – program the ephy rxlos poll internal in milliseconds default 1000 (checkbox).
•Hash Inner Ip Over Gre – control the fields used in the hash for v4/v6 over v4/v6 GRE (checkbox).
•Multiple Tunnel Next Hops – enable multiple tunnel next hops on same port (checkbox).
•L3 Use Host Table – L3 Routes (such as EVPN type 5 routes) use host table for /32 and /128 Routes (checkbox).
•Offline Notification New Thread – When switch goes down thread to send offline notifications (checkbox).
•Uplink Oversubscription Action – nvOS action towards uplink oversubscription (checkbox).
•Flow Tracker Enable – Enable Flow Tracker Feature.
Fabric Manager Services System - Manage System Settings - Modify Settings
Click Save to continue or Cancel to return to the previous screen without making any changes.
Note: Changing any of the following system settings requires a switch reboot:
|
•cpu-class-enable |
|
•optimize-datapath |
|
•single-pass-flood |
A confirmation message displays when these settings are changed.
Click Save to continue or Cancel to return to the previous screen without saving any changes.
About Layer 2 Hardware Hashing
A hardware hashing operation comprises two parts performed at extremely high speed: first, packet field selection and extraction, then a mathematical bitwise computation. Therefore, the first step is for the hardware parsing logic to select a number of packet fields to be hashed depending on the traffic type.
The following table describes the traffic types and related packet fields that the Netvisor ONE OS currently supports by default.
|
Application |
Traffic Type2 |
Hashed Fields3 |
|
Non-IP Packets1 |
Ethernet (a.k.a. ‘Layer 2’) |
Source MAC address, Destination MAC address, Ethertype, VLAN number, source physical port |
|
Plain unicast and multicast IPv4 packets |
IP |
Source IPv4 address, Destination IPv4 address, VLAN number, Destination Layer 4 port, Source Layer 4 port, IP protocol number, source physical port |
|
Plain unicast and multicast IPv6 packets |
IP |
Source IPv6 address, Destination IPv6 address, VLAN number, Destination Layer 4 port, Source Layer 4 port, IP protocol number, source physical port |
|
VXLAN packets (UDP encapsulated) |
IP |
Source IP address, Destination IP address, VLAN number, Destination Layer 4 port, Source Layer 4 port, IP protocol number, source physical port |
|
L2GRE |
IP |
Source IP address, Destination IP address, VLAN number, GRE Key, IP protocol number, source physical port |
|
IPSEC |
IP |
Source IP address, Destination IP address, VLAN number, SPI field, IP protocol number, source physical port |
Notes:
|
• |
1 Certain traffic types such as Mac-in-Mac, FCoE and SCTP are currently not supported for field selection; hence they are not load balanced as opposed to the supported traffic types (see also the next section). |
|
• |
2 Traffic types are based on IANA’s Ethertype definitions (e.g., 0x0800 for IPv4 and 0x86DD for IPv6). Packet fields are based on standard protocol definitions (IEEE 802.3 for Ethernet, RFC 791 and RFC 8200 for IPv4 and IPv6 respectively). |
|
• |
3 (v)LAG hashing applies to bridged as well as routed traffic without distinction. |
About Symmetric Hashing
In addition to regular (asymmetric) hashing, Netvisor ONE supports symmetric hashing for IPv4 and IPv6 traffic. When this mode is enabled, IP traffic is normalized before hashing the fields. That means that the source and destination IP addresses and Layer 4 ports are swapped so that both directions of a bidirectional IP connection are hashed to the same output port in a LAG.
Symmetric hashing’s normalization algorithm has to ignore certain fields that can vary on a per direction basis, such as the VLAN number, protocol value, and the physical ingress interface.
Moreover, as shown in the table above for the Hardware Hashing Field Selection, certain fields such as the GRE key or the IPSec SPI are intrinsically unidirectional. Suppose any GRE or IPSec traffic exists in the network. In that case, Netvisor ONE provides an additional option for symmetric hashing to ignore these unidirectional GRE and IPSec fields so that the normalization only uses source and destination IP addresses and L4 ports for the hash computation.
Symmetric hashing is useful when traffic in both directions needs to be hashed to the same member port in a LAG. This process is required for analysis and correlation purposes or when a monitoring device connected to a member port of a trunk needs to receive a copy of all packets for the connection in both directions.
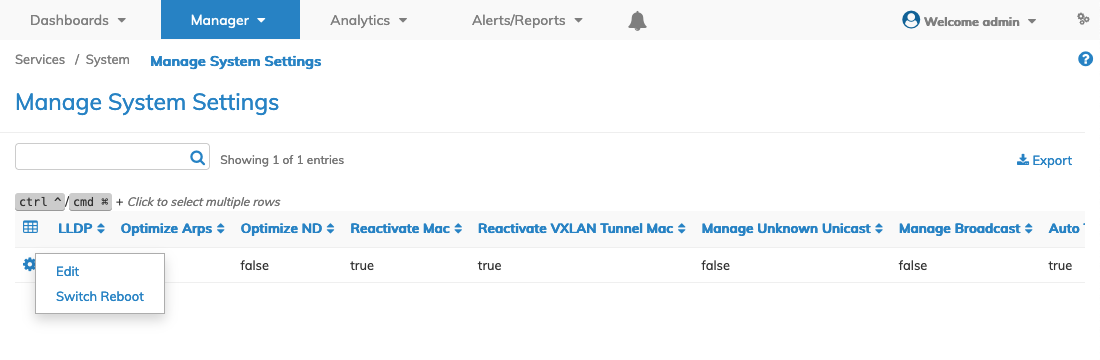
Switch Reboot
To reboot a switch, click Switch Reboot by selecting the choice from the Cog ![]() icon.
icon.
Fabric Manager Services System - Manage System Settings - Reboot Switch
Confirm the Switch Reboot.
Fabric Manager Services System - Manage System Settings - Reboot Switch Confirm
Click OK to delete or Cancel to return to the previous screen without making any changes.
