
vRouter - Manage vRouter
Manager → Layer 3 → vRouter
There are features and functions used in UNUM Manager and UNUM Analytics that are common throughout the user interface (UI). Please refer to the Common Functions section for more information on the use of these functions and features.
vRouters are virtual constructs that handle all Layer-3 traffic in Netvisor ONE switches and fabrics.
UNUM automatically configures vRouters based on the type of playbook chosen when a fabric is built.
In Layer-2 Fabrics, vRouters are created on the spines and the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is configured between the spines.
In Layer-3 Fabrics, vRouters are created on the leafs and the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is configured between the leafs.
In most white-box switching environments, one vRouter will be configured per switch. There are exceptions for this in large environments, or where powerful switches with extra resources are available.
A Virtual Router (vRouter) is an integral part of fabric functionality. For example, for a VLAN to communicate with other VLANs, or networks external to the fabric, it may need a vRouter that spans the internal and the external network.
Fabric-wide vRouter commands can only be executed at the fabric level by the fabric administrator.
Note: For switches with Netvisor ONE, the only available vNET is a global vNET created when creating a fabric for the first time. However, some switches support multiple vNETs based on the platforms. Please refer to the Release Notes for the supported platforms.
Routing protocols essentially work the same way on virtual routers as physical routers.
Note: In the event you need to create a new vRouter, chose the “Hardware” option.
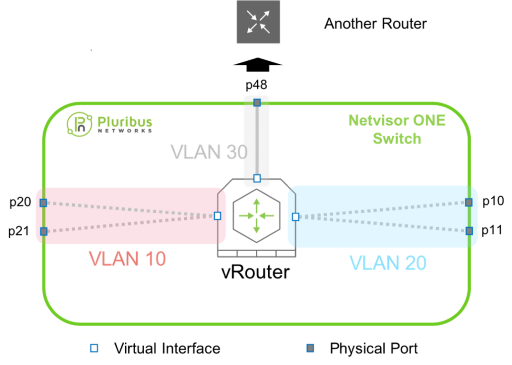
Create a vRouter Example
Example: A vrouter is connected to another vrouter which is mapped to Physical router with port number 48 along with two virtual interfaces for VLAN 10 and VLAN 20
Layer 3 Configuration - vRouter
Manage vRouters
Selecting Manager → Layer 3 → Manage vRouters displays the Manage vRouters dashboard with a list of any existing vRouter settings.
Select the applicable Fabric from the left-hand navigation bar and the dashboard updates showing all vRouter entries from all switches within the Fabric.
Note: If no entries exist a "No Data Exists" message is displayed. You must first configure an entry on a switch. Prerequisite settings and configuration may be required.
This feature table displays data based on the fabric's default Collector Switch. If no data displays in the dashboard, either select a switch from the Left-hand Navigation (LHN) pane or perform a Search by selecting an FRG (Fabric Resource Group) and a specific Attribute from the drop-down lists, as required.
The dashboard displays a list of existing vRouter entries by Fabric.
The Advanced Search function provides a rapid method to search across Fabrics, Fabric Resource Groups and feature Attributes.
Additional parameters include: Switch, Name, Type, Scope,Vnet, State, Router-Type, HW MAC, A-A Routing, HW VR. ID, HW VRRP ID, BGP-AS, Router ID, and EVPN Border.
The vRouter information is scope dependent meaning either Fabric or Local.
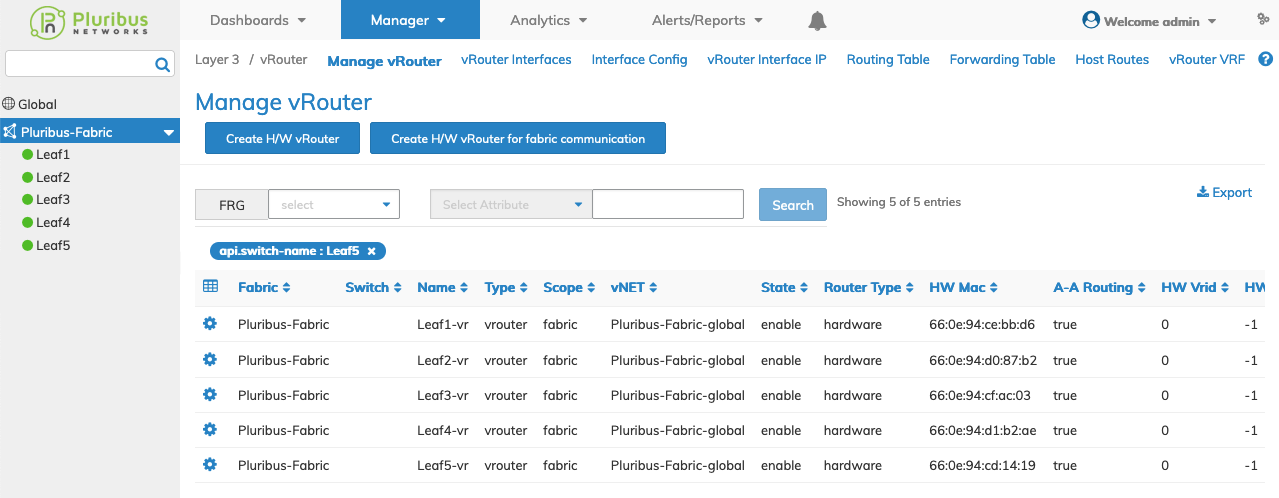
Manager vRouter Fabric Dashboard
Select the applicable switch from the fabric and the dashboard updates automatically with vRouter settings.
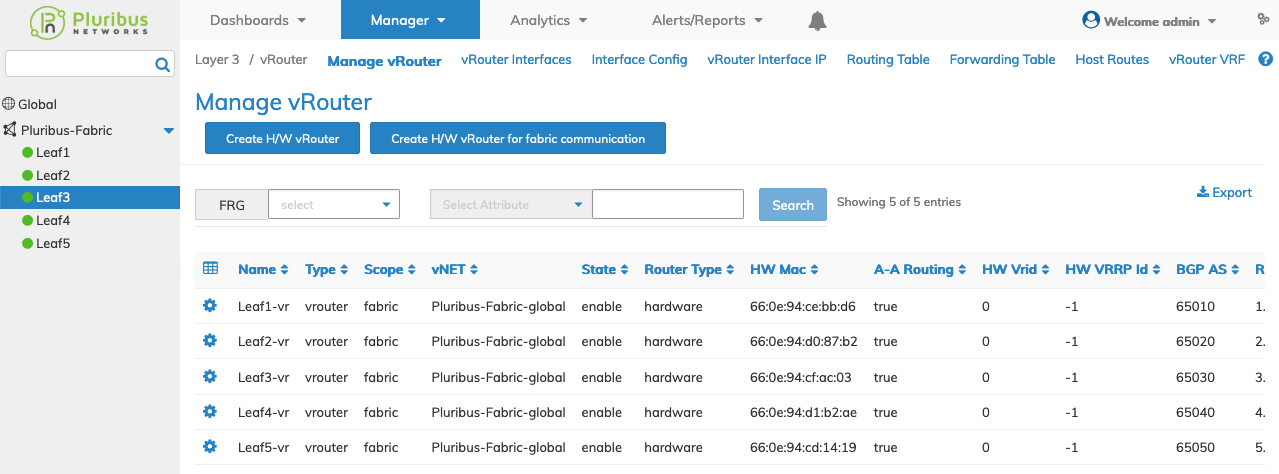
Manager vRouter Switch Dashboard
Select the applicable switch from the fabric. The dashboard displays a list of existing vRouter entries by Name.
Additional parameters include: Type, Scope,Vnet, State, Router-Type, HW MAC, A-A Routing, HW VR. ID, HW VRRP ID, BGP-AS, Router ID, and EVPN Border.
Create vRouters
Hardware and software vRouters are created by selecting either Create H/W vRouter or Create H/W vRouter for Fabric Communication.
Create H/W vRouter
Manager Create vRouter
To create a vRouter enter the configuration parameters which include:
•Switch / FRG – Select the Fabric Resource Group or switch from drop-down list.
•Name – Name of service config.
•Hw Vrrp Id – VRRP ID assigned to the hardware vRouter.
•Router Id – OSPF and BGP router id.
•BGP As – BGP Autonomous System number from 1 to 4294967295.
•Fabric Comm – VRouter for fabric communication (checkbox). Only appears in Create HW vRouter for Fabric Communication menu and creates the vRouter in a local vNET.
•vNet – vNET assigned to service.
•Router Type – Select the vRouter type, software or hardware.
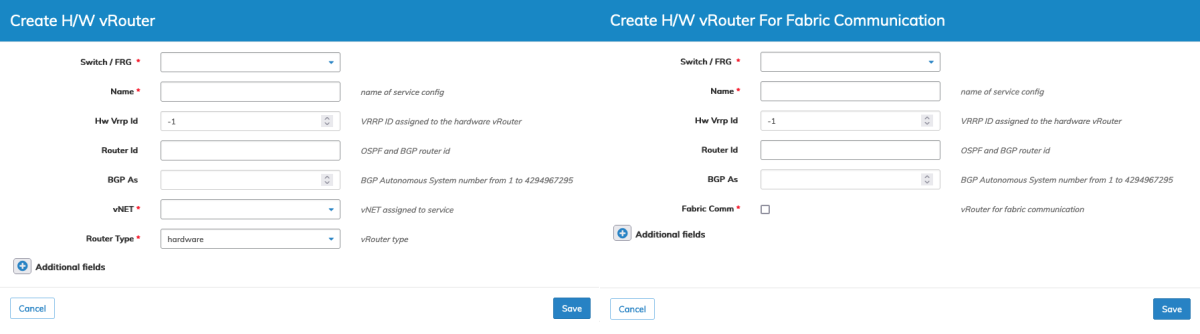
Manager Create vRouter Parameters - Create H/W vRouter & vRouter For Fabric Communications
Click Save to continue or Cancel to return to the previous screen without saving any changes.
Additional Fields
Select additional field parameters by clicking on the ![]() icon. Additional fields include:
icon. Additional fields include:
Additional fields include:
•BGP Redistribute – BGP route redistribution.
•BGP Max Paths – maximum BGP paths.
•BGP iBGP Multipath – number of IBGP multipath connections.
•Shared vNET Mgr – vNET manager to share with if shared service.
•Location – location of service.
•Storage Pool – storage pool assigned to service.
•Router Ipstack – vRouter ipstack.
•EVPN Border – EVPN border node (checkbox).
•EVPN Export All Leaked Networks – exporting leaked subnets to EVPN overlay.
•EVPN Dup Addr Max Moves – EVPN duplicate address max moves.
•EVPN Dup Addr Moves Duration – EVPN duplicate address moves time duration (seconds.)
•EVPN Dup Addr Freeze – EVPN duplicate address freeze duration (seconds).
•Cluster Active Active Routing – active active routing with or without VRRP (checkbox).
•Proto Multi – multicast protocol.
•BGP Redist Static Metric – BGP route redistribution static metric.
•BGP Redist Connected Metric – metric for redistributing BGP connected routes.
•BGP Redist Rip Metric – metric for redistributing RIP connected routes.
•BGP Redist Ospf Metric – metric for BGP to redistribute OSPF connected routes.
•BGP Cluster Id – IP address for BGP cluster ID.
•BGP Bestpath As Path – best path for BGP.
•BGP Dampening – dampening for BGP routes (checkbox).
•BGP Delayed Startup – Delays forming peer adjacency on bootup.
•BGP Network Import Check – Check BGP network route exists in IGP (checkbox).
•BGP Update Delay Strict – Put BGP read only mode on bootup Recommend value less than l3 to vlag delay.
•BGP Keepalive Interval – BGP Keepalive interval (seconds) default 60.
•BGP Holdtime – BGP Holdtime (seconds) default 180.
•BGP Distance External – BGP distance for routes external to AS.
•BGP Distance Internal – BGP distance for routes internal to AS.
•BGP Distance Local – BGP distance for local routes.
•Ospf Spf Delay – Delay (msec) from first change received till SPF calculation.
•Ospf Spf Consec Delay – Initial hold time (msec) between consecutive SPF calculations.
•Ospf Spf Max Delay – Maximum hold time (msec).
•Ospf6 Spf Delay – Delay (msec) from first change received till SPF calculation.
•Ospf6 Spf Consecu Delay – Initial hold time (msec) between consecutive SPF calculations.
•Ospf6 Spf Max Delay – Maximum hold time (msec).
•BGP Global Nh Preference – use global nexthop preference for choosing nexthop type in BGP ipv6.
•Rip Redistribute – redistribute RIP routes.
•Ospf Redistribute – redistribute OSPF routes.
•Ospf Redist Static Metric – metric for OSPF redistribution of static routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist Static Metric Type – metric type for OSPF redistribution of static routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist Connected Metric – metric for OSPF redistribution of connected routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist Connected Metric Type – metric type for OSPF redistribution of connected routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist Rip Metric – metric for OSPF redistribution of RIP routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist Rip Metric Type – metric type for OSPF redistribution of RIP routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist BGP Metric – metric for OSPF redistribution of BGP routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Redist BGP Metric Type – metric type for OSPF redistribution of BGP routes (IPv4 only).
•Ospf Distance External – OSPF distance for external routes.
•Ospf Distance Internal – OSPF distance for inter area routes.
•Ospf Distance Local – OSPF distance for intra area routes.
•Ospf Stub Router On Startup – advertise self as stub router temporary on startup (checkbox).
•Ospf Stub Router On Startup Period – period to advertise self as stub router after startup.
•Ospf Bfd All If – use BFD protocol for fault detection on all OSPF interfaces (checkbox).
•Ospf Default Information – control origination of default route.
•Ospf Default Info Originate Metric – metric for OSPF origination of default route.
•Ospf Default Info Originate Metric Type – metric type for OSPF origination of default route.
•Vrrp Track Port – track port for VRRP.
•BGP Default Shutdown – Apply administrative shutdown to newly configured peers (checkbox).
•BGP Snmp – Enable BGP SNMP MIB (checkbox).
•BGP Snmp Notification – Enable BGP SNMP notifications (checkbox).
•Ospf Snmp – Enable OSPF SNMP MIB (checkbox).
•Ospf Snmp Notification – Enable OSPF SNMP notifications (checkbox).
•Ospf6 Snmp – Enable OSPFv3 SNMP MIB (checkbox).
•Ospf6 Snmp Notification – Enable OSPFv3 SNMP notifications (checkbox).
•Ip Snmp – Enable ipForward SNMP MIB (checkbox).
•No BGP Redist Static Route Map – Remove route map for BGP static redistribution (checkbox).
•No BGP Redist Connected Route Map – Remove route map for BGP connected redistribution (checkbox).
•No BGP Redist Ospf Route Map – Remove route map for BGP OSPF redistribution (checkbox).
•BGP Graceful Shutdown – BGP graceful shutdown RFC 8326 (checkbox).
Modify a vRouter
To modify a vRouter use Edit by selecting the Cog ![]() icon to make required changes to the vRouter parameters.
icon to make required changes to the vRouter parameters.
•Router Id – OSPF and BGP router ID.
•BGP As – BGP Autonomous System number from 1 to 4294967295.
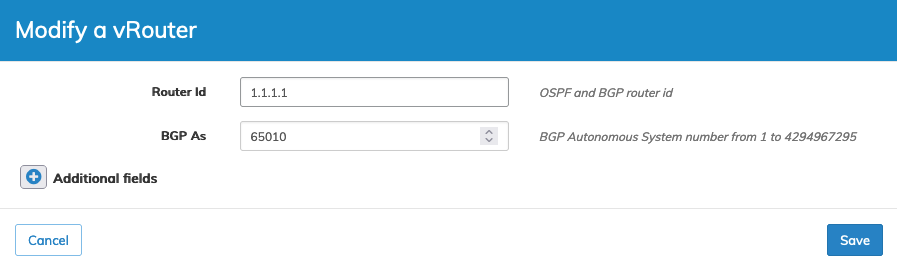
Manager Layer 3 Modify vRouter
Click Save to continue or Cancel to return to the previous screen without saving any changes.
Select additional field parameters by clicking on the ![]() icon. Additional fields include:
icon. Additional fields include:
See the Create a H/W vRouter list above for parameter details.
Delete a vRouter
To delete a vRouter use Delete by selecting the Cog ![]() icon.
icon.
A confirmation message requires an acknowledgment to continue deletion.
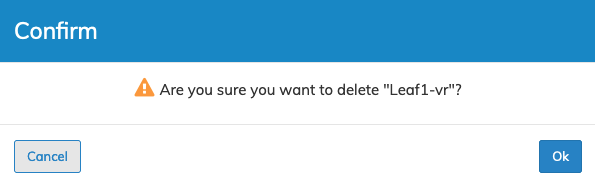
Manager Delete vRouter Confirmation Message
Click OK to continue or Cancel to return to the previous screen without making any changes.
